AFM can operate in number of
modes, depending on the application. Generally, possible imaging modes are
divided into:
1)
static a.k.a. contact mode and
2)
dynamic mode which can be devided into:
a.
Non-contact
and
b.
Tapping mode.
In dynamic or non-contact mode
cantilever vibrates.
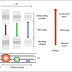
STATIC MODE
Static or contact mode of
operation is a mode in which the static tip deflection is used as a feedback
signal. The reason for that is measurement of static signal is prone to noise
and drift. Cantilevers with low stiffness are used to boost the deflection
signal. When the tip of the cantilever is close to the surface of a sample,
attractive forces between tip atoms and sample atoms can be quite strong
causing the tip to dive into sample. Thus the static mode of AFM is always done
in contact where the overall force is repulsive. For that reason this AFM
scanning method is also called contact mode. In this cotact mode, the force
between the tip and the surface is kept constant during scanning by maintaining
constant deflection.
Advantages of this mode:
-
Relatively fast scanning speed,
-
scaning rough samples and
-
good for friction analysis studies.
Disadvantage of this method is
that the forces can damage or deform soft samples but imaging soft samples in
liquids in most cases will reslove this issue.
Figure 1 – Contact and
non-contact mode
DYNAMIC MODES
TAPPING MODE
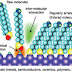
Mode whcih lies between contact
and non-contact mode is tapping mode. In this mode the cantilever is oscillated
at its resonant frequnecy. The probe lightly taps on the sample surface during
scanning, contacting the surface at the bottom of its swing. By maintaining
constant oscillation amplitude a constant tip-sample interaction is maintained
and an image of the surface is obtained.
Figure 2 – Tapping mode
Advantages of tapping mode is
that it allows a high resolution of samples that are easily damaged or only
loosely held to the surface. So it's convinient for most biological samples.Disadvantage is that It's more
challenging to image in liquids using tapping mode.
NON-CONTACT MODE
In non-contact mode, th tip of the cantilever insn't in contact with the sample surface. The cantilever vibrates at or just above its resonant frequency. The amplitude of oscillation is typically a few nanometers down to a few picometers. Van der Waals forces which extend above the surface act to decrease the resonance frequency of the cantilever. This decrease in resonant frequency combined with the feedback loop system maintains a constant oscillation amplitdue or frequency by adjusting the average tip-to-sample distance. Measuring tip-to-sample distance at each (x,y) data point allows scanning software to construct topographic image of the sample surface.
Advantages of non-contact mode:
1) exerts very low force on the sample (10^-12N) which makes non-contact AFM preferable for measuring soft sample, such as biological samples and organic thin fils.
2) AFM is the extended probe lifetime. Non-contact mode AFM does not suffer from tip or sample degradation effects that are sometimes observed after taking numerous scans with contact AFM.
Disadvantages of non-contact mode:
Contaminat layer on the surface can interfere with oscillation and for optimal imaging with non-contact mode and ultra-high vacuum (UHV) is generally required.
Following video demonstrates Non-contacting mode.
- Lower resolution, (if a few monolayers of adsorbed fluid are lying on the surface of a rigid sample, the images may look quite different) In case of rigid samples contact and non-contact mode images look the same.
Contaminat layer on the surface can interfere with oscillation and for optimal imaging with non-contact mode and ultra-high vacuum (UHV) is generally required.
Following video demonstrates Non-contacting mode.






0 comments:
Post a Comment