Atomic
force microscopy or Scanning force microscopy is very high resoultion type of
scanning probe microscopy. The atomic force microscopy was invented in 1986. by
Binning and coworkers. Resolution of this high powered microscope is fraction
of a nanometer which is about 1000 times smaller than optical diffraction limit.
We can say that AFM is generating information by “feeling” the surface with a
mechanical probe. To ensure very precise scanning piezoelectric elements are
used because they facilitate accurate and precise tiny movements. Using
conducting cantilevers in AFM the electric potentials can also be scanned.With
AFM you can measure mechanical contact, van der Waals, capillarity, chemical
bonds, electrostatic and magnetic forces. Along with the force, additional
quantities may simultaneously be measured through the use of specialized types
of probes.
Figure 1 – Atomic force microscope
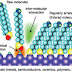
The AFM consists of a cantilever with a sharp
tip or probe at its end and this probe is used to scan specimen surface. Thipically
the cantilever is made from silicon or silicon nitrade with a tip radius of
curvature on the order of nanometers.
Figure 2 – Cantilever of AFM
Figure 3 – Cantilever with a tip
Besides this we can simultaneously measure
additional quantities using specialized types of probes. The deflection of
cantilever is measured using a laser spot which is reflected from the top
surface of the cantilever into an array of photodiodes.
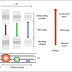
Figure 4 – Schematic diagram of AFM surface
scanning
The
previous figure shows basic elements of AFM and this elements are: Cantilever,
Laser, and photodiode or an array of photodiodes. The main part of AFM is
cantilever which is in contact with the sample surface. At the end of the
cantilever is a tip with curvature radius of a few nanometers and generally
they are made from silicon or silicon nitride. When the tip is brought into
proximity of a sample surface, forces between the tip and the sample lead to
deflection of the cantilever. The laser beam is used to measure deflection
because the laser spot is reflected from the top surface of the cantilever into
a photodiode.
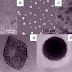
The result of AFM is a map that represents the
topography of the sample.
Figure 5 - Atomic force microscope
topographical scan of a glass surface.
Sample
is usually mounted on the piezoelectric tube that can move the sample in z
direction in order to maintain a constant force, and the x and y directions to
scan the sample. There is also a tripod configuration of three piezo crystals
that may be employed, with one responsible for scanning in each of the x,y and
z directions. Newer designs have tip mounted on a vertical piezo scanner while
the sample is being scanned in x and y using an addition piezo block. The
result in AFM is topography of the sample. The lateral resolution using AFM
tools can be up to 0.1 nm while the vertical resolution can be up to 0.02 nm.
Following video explains how the AFM works.
Following video explains how the AFM works.







0 comments:
Post a Comment