In order to validate the sensor the sensing result are
fulfilled by characterizing one or combination of the following parameters:
- Accuracy – Comparison between the measured results and the true value
- Precision – Is measure of how scattered the results are around the average value,
For a sensors to be accurate and precise, the measures
result should be gathered around the average value and also be clustered
together.
- Sensitivity – Indicates the extent of change in a sensor’s output when the measured quantity varies. Sensors that measure very small changes must have very high sensitivities. The sensitivity of the sensor is define as the slope of the output characteristic curve.
- Detection limit is the lowest measured value or lowest concentration that can be detected by the sensor, following a previously defines signal-to-noise ratio. In reality every device has some amount of noise at its output. However it the signal level is very low noise level can have adverse effect.
- Signal-to-noise ratio is a way to appreciate if the signal is strong enough compared to the noise. This requires two measurement followed by a simple calculation. The first step is the measurement of the device output level under test with no input signal. The second step is to apply a signal to the device and to take another level measurement. The deviation of the two results will output the signal to noise ratio. The detection limit is generally defined as the measured value that provides a signal-to-noise ratio of approximately 3.
- The limit of quantitation is a term used to describe the lowest concentration at which the analyte can not only be reliably detected but at which some predefined goals for bias and imprecision are met.
- Dynamic Range – A term describing the measureable maximum and minimum values of the applied parameter. Each sensor is described to work over a specified range. Dynamic ranges are generally fixed values, and if exceeded, result in permanent damage to or destruction of a sensor.
It
is customary to use transducing elements over only the part of their range
where they provide predictable performance and often enhanced linearity.
- Linearity – is the relative deviation of sensing behavior from an ideal straight line. Ideal sensors are designed to be linear or liner to some simple mathematical function of the measurement, typically logarithmic. In practice, the relationship between the measured value and output of most transducers is not perfectly linear and it is therefore necessary to find a way of using these device to achieve the most accurate overall results. This can be achieved by constructing what is known as the straight line”.
- Selectivity refers to characteristics that determine whether a sensor can respond selectively to a group of analytes or even specifically to a single analyte. For example, when an ideal selective sensor is exposed to a mixture of molecules, it interacts with those for which the sensor is selective and rejects the interfering molecules.
- Resolution is the smallest detectable incremental change of the input parameter that can be detected in the output signal. Often in a digital display, the least significant digit will fluctuate, indicating that changes of that magnitude are only just resolved.
- Response time is the time taken by a sensor to approach its true output when subjected to a step change in input. Response time is generally specified as the time necessary for the output to rise to 90% of the final value, measured from the onset of the measured variable step input change.
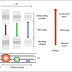
- Hysteresis refers to the inability to faithfully repeat recorded data output when measuring a range of values and scanning from different directions. Hysteresis is a major problem in sensing applications as two signals might be obtained for the same concentration, for example, depending on the directionality of the concentration as shown in next figure.





0 comments:
Post a Comment