Acoustic levitation is a method
for suspending matter in a medium by using acoustic radiation pressure form
intense sound waves in the medium. Acoustic levitation is possible because of
the non-linear effects of intense sound waves.
Today this type of levitation is
usually used for containerless processing which has become more important due
to the small size and resistance of microchips and other things in industry.
Containerless processing may also be used for application which requires
high-purity materials or chemicla reactions too rigorous to happen in
container. This method is very hard to control than other methods of
containerless processing such as electromagnetic levitation but has an
advantage of being able to levitate nonconducting materials.
But how acoustic levitation
works?
The concept of levitating small
particles by acoustic radiation pressure was proposed as early as 1934 by King.
He was the pioneer who made theoretical foundation of acoustic levitation.
However, it was not until the 1970's that acoustic drivers wer sufficiently
powerful to allow practical application of acoustic levitators. As i mentioned
earlier, the acoustic levitation is ued for containerless materials processing and
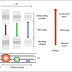
space shuttle experiments. In a typical levitator, shown in nex picutre, an
acoustic standing wave is generated between a transmitter and a reflector
separated by an integral number of half wavelengths. The particle is supported
against gravity by the pressure forces and tends towards a stable equilibrium
position in the vicinity of the acoustic nodal planes. The reflector needs to
be curved to a point within the nodal plane that lies along the axis of the
device. Thus, both verical and horizontal stability is achieved with a single
device.
Acoustic levitation holds several
unique advantages over conventional experimental techniques (e.g. vertical wind
tunnels, free fall testing, mechnaincal suspension or in situ measurement). The
principal advantage of the acoustic levitation technique is the ability to
support particles in a precise manner for indefinete periods of time. The
stabilty in position control for a typical vertical levitator is on the other
of one droplet diameter or less. This is in marked contrast to vertical wind
tunnels, where the small scale of the droplet, compared with the mean and
turbulet flow scales, make percies positioning difficult. The stedy and
repeatable nature of the support allows invetigation of microphysical behaviour
such as phase change or hydrometeor evolution which may occur on time scales of
minutes. Experiments of this type are extremly difficult in vertical wind
tunnels and impossible in free fall testing.
The net force on the object which
is subjected to an acoustic field arises from the nonlinear realtionship
between the instantaneous pressure and velocity in an acoustic medium. Under
certain condition, this nonlinearity can produce significant pressure gradients
over the surface of an object, resulting in an appreciable net force on it. As
a result, sufficinetly strong acoustic fields can suspend object against the
force of gravity, making it possible to stady the object in a contact-free
environment.



0 comments:
Post a Comment